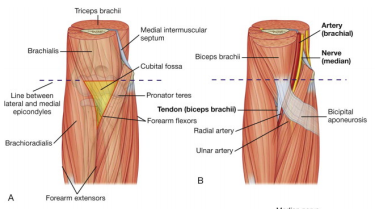
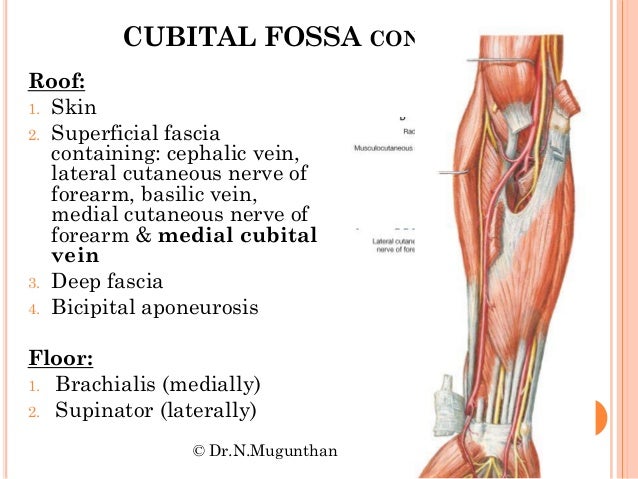
The floor of the fossa is formed by the brachialis muscle proximally and the supinator muscle distally the roof from superficial to deep forms from the skin fascia and the bicipital aponeurosis.
Cubital fossa roof and floor.
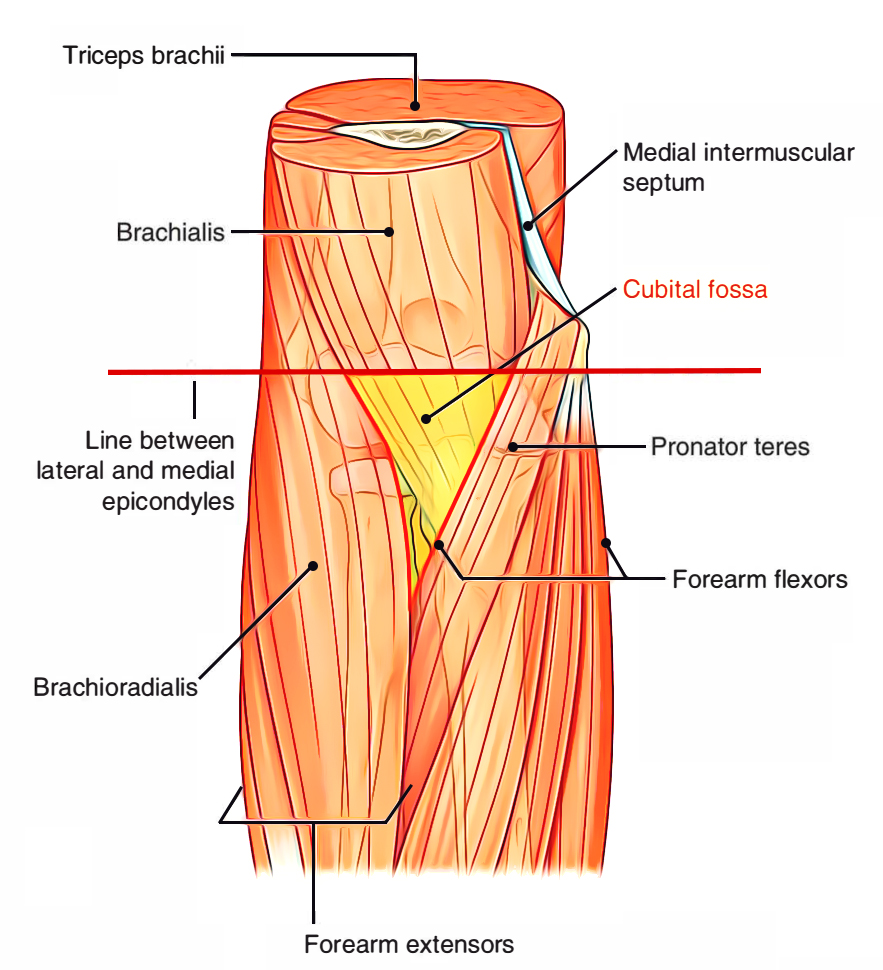
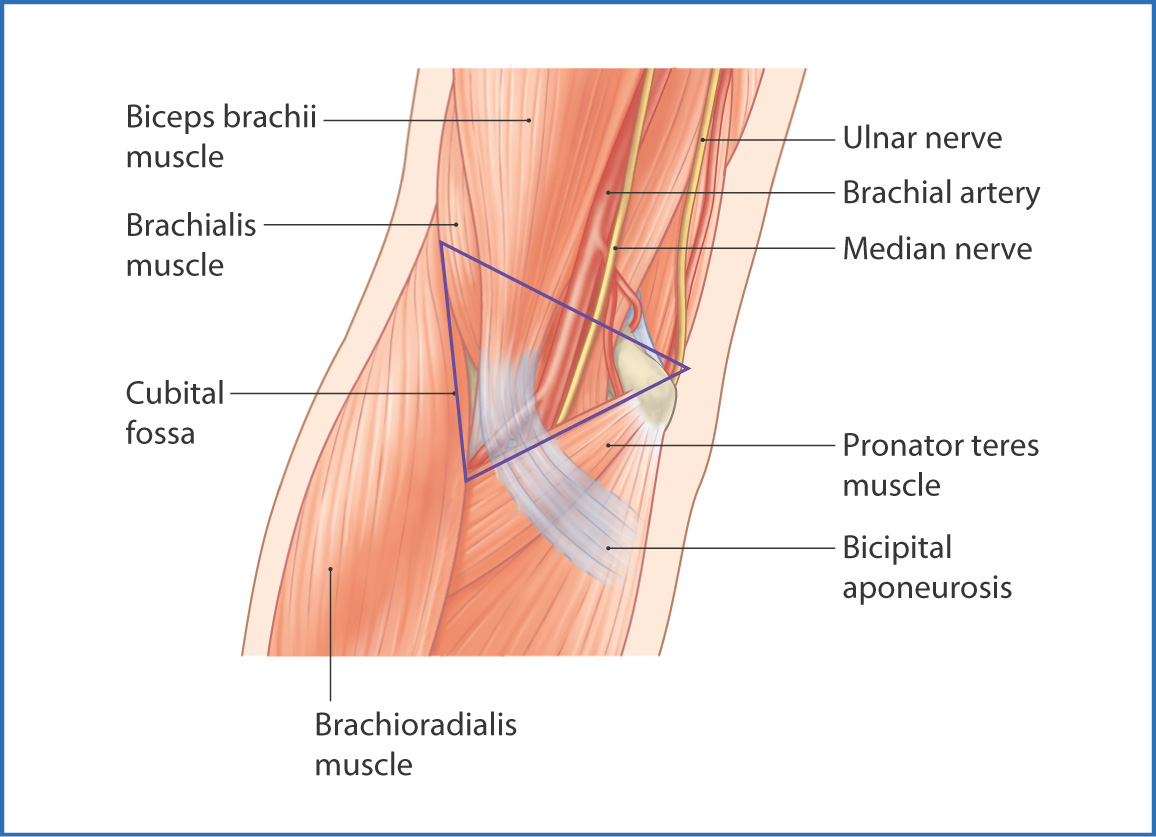
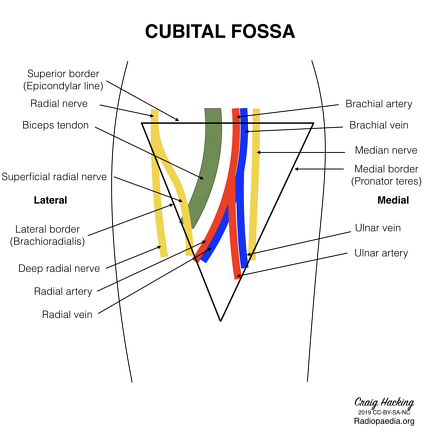
Prof nabil ebraheim university of toledo ohio usa the cubital fossa is a triangular depression located in front of the anterior elbow the medial border is formed by the pronator teres which arises from the medial epicondyle of the humerus the lateral border is formed by the brachioradialis muscle which arises from the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus the meeting of these.
It is also known as the antecubital because it lies anteriorly to the elbow.
It also has a floor and roof and it is traversed by structures which make up its contents.
It is pierced by a communication between the deep veins and the median cubital vein.
Contents of cubital fossa.
The cubital fossa chelidon or elbow pit is the triangular area on the anterior view of the elbow of a human or other hominid animal.
The roof of the cubital fossa is formed by.
Skin superficial fascia containing the median cubital vein the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm and the medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm.
Its boundaries roof floor and contents.
It has three boundaries borders and it also has a floor.
Borders the floor of the cubital fossa is formed proximally by the brachialis and distally by the supinator muscle.
The cubital fossa is triangular in outline with the base above.
It is covered by the skin and by superficial fascia containing a portion of the cephalic vein a portion of the basilic vain.
The roof is the deep fascia strengthened by the bicipital aponeurosis.
The antecubital fossa is a triangular space on the anterior aspect of the forearm.
It lies very superficially within the roof of the cubital.
The roof consists of skin and fascia and is reinforced by the bicipital aponeurosis.
I have discussed complete anatomy of cubital fossa.
Superiorly by an imaginary line between the medial and lateral epicondyles.
Medially by pronator teres.
Deep fascia bicipital aponeurosis.
Within the roof runs the median cubital vein which can be accessed for venepuncture see clinical relevance below.
The triangular borders are formed.
Deep boundary floor brachialis and supinator muscles.
Roof skin.
It is a space filled with different structures that makes up its content.
The floor of the cubital fossa is formed proximally by the brachialis and distally by the supinator muscle.
The roof consists of skin and.
I discuused all nerves arteries which passes from cubital fossa.
Venepuncture one of the most commonly used sites is the median cubital vein.
The cubital fossa contains four main vertical structures from lateral to medial.
The roof of the fossa is formed by subcutaneous tissue.